
Sustainable Defensible Space — Landscape Design for Fire Protection in the (Coastal) Western US
A webinar that provided detailed information about the principles homeowners can apply to create fire-wise landscapes that are both sustainable and defensible.
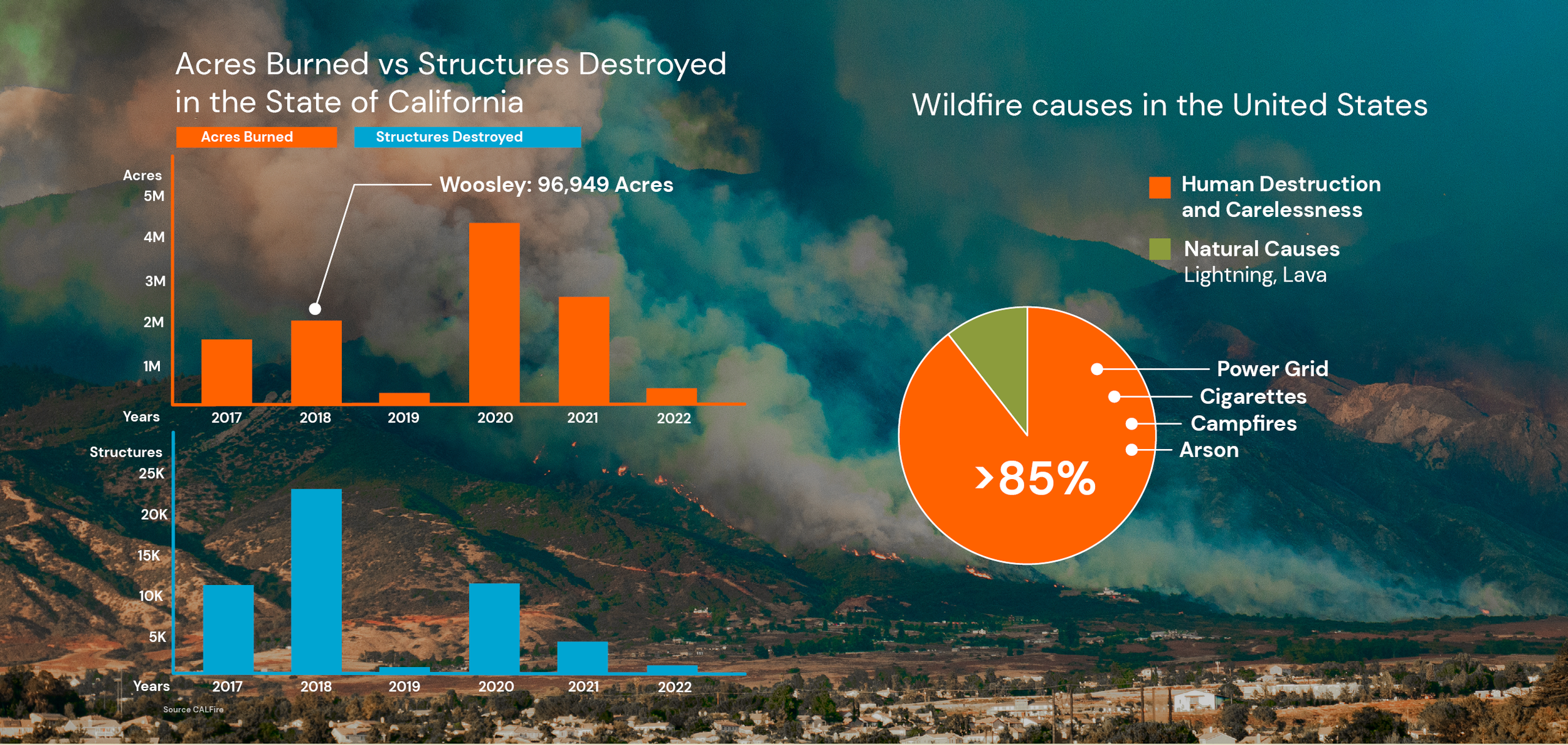
The area most severely affected by fire is the Wild Urban Interface (WUI), where human residence abuts wildlands and our focus of Southern California, one of the richest habitats in the world is also one of the most fire-prone and inhabitted areas. Our presentation goes in detail about fire preparedness: where wildfire occurs, how it behaves, how it affects the ecology. Provides solutions for how to reduce fire risk for structures while sustainably landscapeing, and the importance of maintenance and community-wide coordination.
Southern California has the most rapidly expanding urban areas in the United states such as the Los Angeles basin, Orange County, and the greater San Diego area, continued habitat loss and fragmentation threaten the long-term existence of many native species and pose the greatest threats to biodiversity.
Overlay of Fire Severity Zones, habitat and urban sprawl gives a clear picture of how intact habitat is lost, the numbers of rare, threatened, and endangered species rise resulting on invasion of nonnative weeds that produce lighter, more flammable fuels.
Laddering Effect Plants protect soils from erosion and provide aesthetic and ecological benefits. Proper landscape maintenance can dramatically improve the fire safety of structures and landscapes.
Trees and shrubs are acceptable as long as they are widely spaced and do not provide a continuous path of fuel for a fire to climb from the ground to a tree crown or roof (a fuel ladder). Grazing herds, like goats, not only reduces fuel but increases biodiversity.
Examples of California native plants that have fire-wise characteristics.
Examples of California appropriate plants that have fire-wise characteristics.






